ATL Labor Market Information
Occupational Information Network (O*NET)
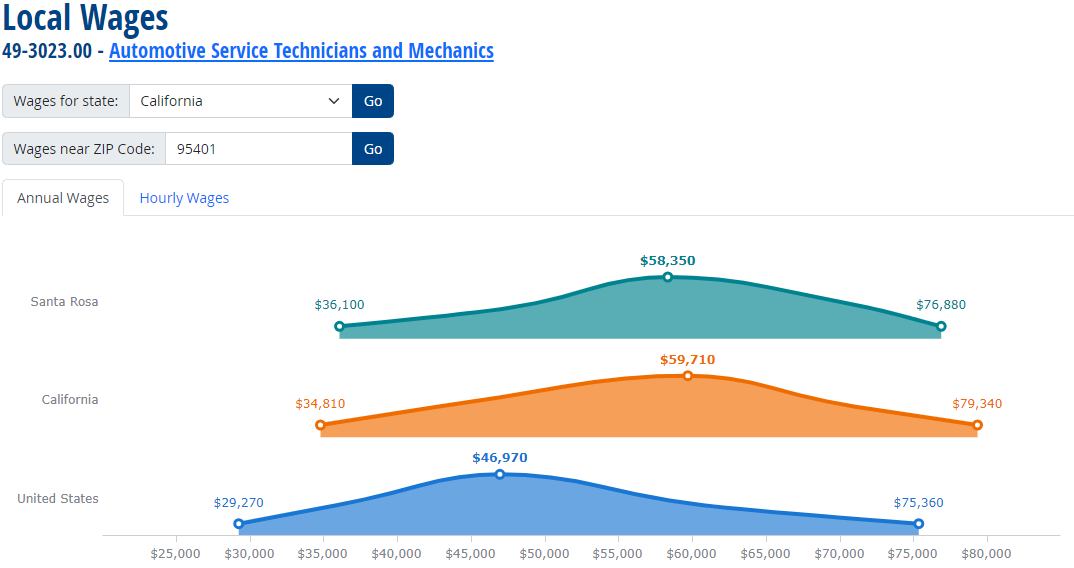
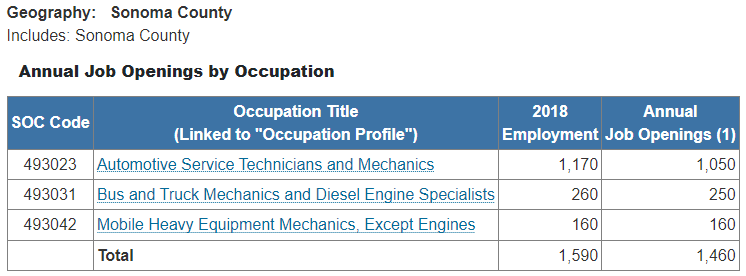
Automotive Service Technicians and Mechanics
Standard Occupational Classification: 49-3023.00
Job Description: Diagnose, adjust, repair, or overhaul automotive vehicles.
Sample of reported job titles:
- Automotive Drivability Technician (Auto Drivability Tech)
- Automotive Mechanic (Auto Mechanic)
- Automotive Service Technician (Auto Service Tech)
- Automotive Technician (Auto Tech)
- Diagnostic Technician (Diagnostic Tech)
- Heavy Line Technician (Heavy Line Tech)
- Lube Tech (Lubrication Technician)
- Mechanic
- Quick Service Technician (Quick Service Tech)
- Service Technician (Service Tech)
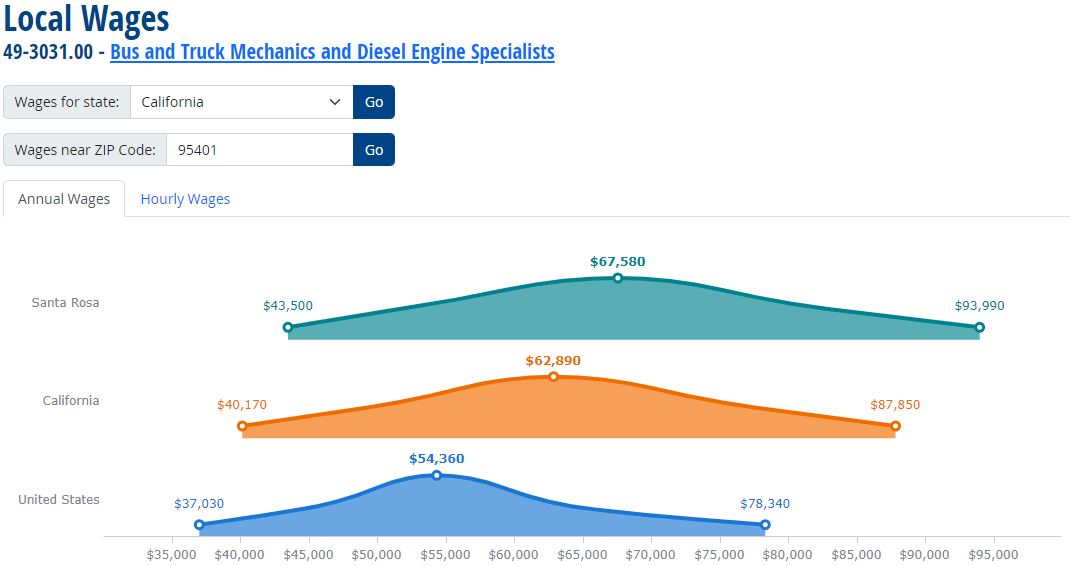
Bus and Truck Mechanics and Diesel Engine Specialists
Standard Occupational Classification: 49-3031.00
Job Description: Diagnose, adjust, repair, or overhaul buses and trucks, or maintain and repair any type of diesel engines. Includes mechanics working primarily with automobile or marine diesel engines.
Sample of reported job titles:
- Bus Mechanic
- Diesel Mechanic
- Diesel Technician (Diesel Tech)
- Fleet Mechanic
- General Repair Mechanic
- Heavy Truck Mechanic
- Service Technician
- Trailer Mechanic
- Transit Mechanic
- Truck Mechanic
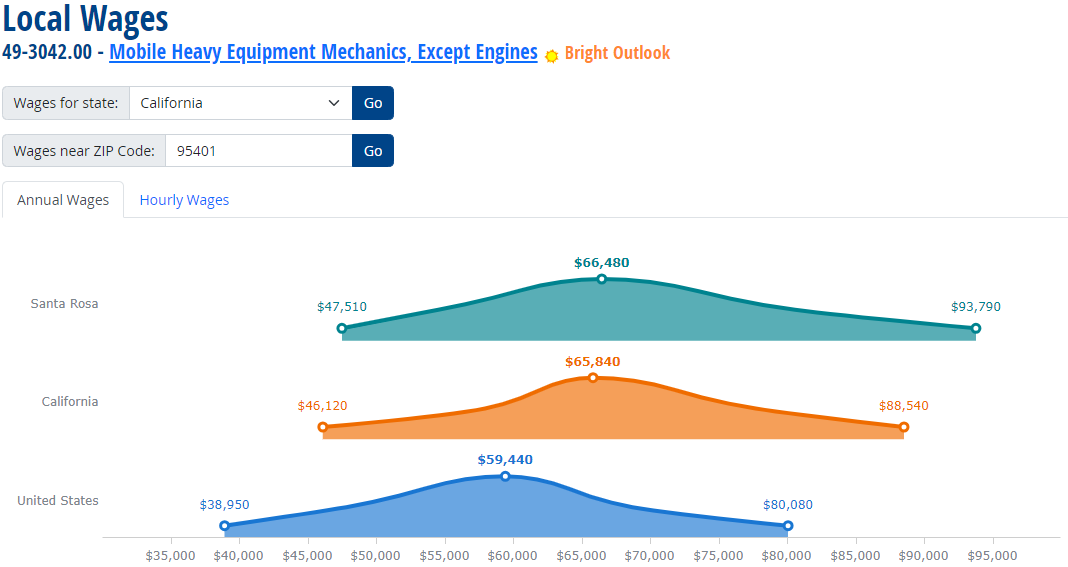
Mobile Heavy Equipment Mechanics, Except Engines
Standard Occupational Classification: 49-3042.00
Job Description: Diagnose, adjust, repair, or overhaul mobile mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic equipment, such as cranes, bulldozers, graders, and conveyors, used in construction, logging, and mining.
Sample of reported job titles:
- Construction Equipment Mechanic
- Equipment Mechanic
- Equipment Technician
- Field Mechanic
- Field Service Technician
- Field Technician
- Heavy Equipment Mechanic
- Heavy Equipment Technician
- Mechanic
- Mobile Heavy Equipment Mechanic
Tasks
- Inspect vehicles for damage and record findings so that necessary repairs can be made.
- Test drive vehicles and test components and systems, using equipment such as infrared engine analyzers, compression gauges, and computerized diagnostic devices.
- Test and adjust repaired systems to meet manufacturers' performance specifications.
- Use handtools, such as screwdrivers, pliers, wrenches, pressure gauges, or precision instruments, as well as power tools, such as pneumatic wrenches, lathes, welding equipment, or jacks and hoists.
- Review work orders and discuss work with supervisors.
Work Activities
- Getting Information — Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Operating Vehicles, Mechanized Devices, or Equipment — Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or watercraft.
- Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge — Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
- Repairing and Maintaining Mechanical Equipment — Servicing, repairing, adjusting, and testing machines, devices, moving parts, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of mechanical (not electronic) principles.
- Making Decisions and Solving Problems — Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
- Operating Vehicles, Mechanized Devices, or Equipment — Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or watercraft.
Skills
- Repairing — Repairing machines or systems using the needed tools.
- Troubleshooting — Determining causes of operating errors and deciding what to do about it.
- Critical Thinking — Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions, or approaches to problems.
- Operations Monitoring — Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
- Equipment Maintenance — Performing routine maintenance on equipment and determining when and what kind of maintenance is needed.
Knowledge
- Mechanical — Knowledge of machines and tools, including their designs, uses, repair, and maintenance.
- Mathematics — Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
- Computers and Electronics — Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
- Customer and Personal Service — Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
- Engineering and Technology — Knowledge of the practical application of engineering science and technology. This includes applying principles, techniques, procedures, and equipment to the design and production of various goods and services.
Abilities
- Deductive Reasoning — The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
- Control Precision — The ability to quickly and repeatedly adjust the controls of a machine or a vehicle to exact positions.
- Manual Dexterity — The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects.
- Finger Dexterity — The ability to make precisely coordinated movements of the fingers of one or both hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble very small objects.
- Extent Flexibility — The ability to bend, stretch, twist, or reach with your body, arms, and/or legs.
- Inductive Reasoning — The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
- Near Vision — The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Work Styles
- Attention to Detail — Job requires being careful about detail and thorough in completing work tasks.
- Dependability — Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations.
- Integrity — Job requires being honest and ethical.
- Analytical Thinking — Job requires analyzing information and using logic to address work-related issues and problems.
- Independence — Job requires developing one's own ways of doing things, guiding oneself with little or no supervision, and depending on oneself to get things done.